Map of South Dakota
The state of South Dakota is located in the North Central region of the United States. South Dakota is bordered by North Dakota to the north, Minnesota to the east, Iowa to the southeast, Nebraska to the south, Wyoming to the west, and Montana to the northwest.
About the map:
This map of South Dakota State shows the state borders, states, state capital, county borders, counties, county seats and important cities.
County seats are indicated by a red circle, white circles indicate cities, and the capital of South Dakota is indicated by a star in the red circle. The larger the city in terms of population, the larger the circle on the map and the larger the font of the city name.
Attribution is required! You may download, print or use the above map for educational, personal and non-commercial purposes. You must place a hyperlink (to this page) with attribution next to the image you use.
South Dakota State Maps
Other Maps of South Dakota
South Dakota State Profile

The Great Seal of the State of South Dakota |

Flag of South Dakota |
| Capital: | Pierre |
| Largest city: | Sioux Falls |
| Largest metropolitan area: | Sioux Falls |
| Largest county by population: | Minnehaha County |
| Largest county by area: | Meade County |
| Area: | 77,116 sq mi (199,729 km2) |
| Population (2024): | 924,669[1] |
| Density: | 11.5/sq mi (4.44/km2) |
| Dimensions: |
|
| Latitude: | 42°29′ N to 45°56′ N |
| Longitude: | 96°26′ W to 104°03′ W |
| Elevation: |
|
| Official language: |
|
| Religion (2022):[2] |
|
| Racial/ethnic groups (2024):[1] |
|
| Median household income (2023): | $72,421[1] |
| USPS abbreviation: | SD |
| ISO 3166 code: | US-SD |
| Time zone: |
Eastern half: UTC−06:00 (Central) Summer (DST) UTC−05:00 (CDT) Western half: UTC−07:00 (Mountain) Summer (DST) UTC−06:00 (MDT) |
| The Official Website of the State of South Dakota: | www.sd.gov |
About the State of South Dakota
South Dakota is a U.S. state located in the North Central region of the United States. It ranks 17th in area among U.S. states, covering 77,116 square miles (199,729 km²). South Dakota borders North Dakota to the north, Minnesota and Iowa to the east, Nebraska to the south, and Wyoming and Montana to the west. The state has a population of 924,669 (2024), making it the 5th least populous state in the nation.
Pierre serves as the state capital, while Sioux Falls functions as the largest city with a population of 209,289 (2024 estimate). Other significant urban centers include Rapid City (78,863), Aberdeen (28,495), and Brookings (24,794). The Missouri River divides South Dakota into two distinct regions known locally as "East River" and "West River."
The economy of South Dakota relies primarily on agriculture, tourism, and defense spending. Agricultural products include cattle, corn, soybeans, wheat, and hogs. The state contains significant natural resources, particularly gold, and produces ethanol, wind energy, and hydroelectric power. South Dakota maintains one of the lowest unemployment rates in the United States and does not levy a state income tax.
Ellsworth Air Force Base near Rapid City constitutes a major economic contributor, housing B-1 bombers and employing thousands of military and civilian personnel. Financial services also play a substantial role in the state's economy, with Citibank establishing its credit card operations in Sioux Falls following favorable banking regulation changes in the 1980s.
Tourism generates approximately $2 billion in annual economic activity. The state attracts visitors to numerous attractions, including Mount Rushmore National Memorial, which features 60-foot granite sculptures of four U.S. presidents. Other significant destinations include Badlands National Park, known for its eroded buttes and pinnacles, Wind Cave National Park, which contains one of the world's longest cave systems, and Custer State Park, home to one of North America's largest publicly owned bison herds.
The Black Hills region in western South Dakota draws numerous tourists with its combination of natural beauty and attractions such as Deadwood, a historic gold mining town. The annual Sturgis Motorcycle Rally brings hundreds of thousands of visitors to the state each August.
Native American reservations occupy significant portions of South Dakota, including Pine Ridge, Rosebud, Cheyenne River, and Standing Rock. These sovereign territories maintain their own governments while existing within state boundaries.
Brief History
South Dakota entered the Union as the 40th state on November 2, 1889, simultaneously with North Dakota. The region's history extends thousands of years before European contact, with indigenous nations including the Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota establishing complex societies throughout the area. Archaeological evidence indicates human habitation dates back approximately 11,500 years.
European exploration began when French fur traders arrived in the early 18th century. The United States acquired the territory through the Louisiana Purchase of 1803, and the Lewis and Clark expedition traversed the region in 1804-1806, documenting its geography and native populations. American settlement increased slowly following these explorations.
The U.S. government established Dakota Territory in 1861, encompassing present-day North and South Dakota, Wyoming, and Montana. White settlement accelerated after the discovery of gold in the Black Hills in 1874, precipitating conflicts with indigenous nations who held these lands sacred. The Great Sioux War culminated in the U.S. Army's defeat at the Battle of Little Bighorn in 1876.
Railroads transformed the territory in the 1880s, bringing thousands of European immigrants who established farms and ranches across the eastern plains. Agricultural development coincided with the systematic displacement of Native Americans onto reservations. The tragic Wounded Knee Massacre in 1890 marked a devastating chapter in this history.
Early statehood featured agricultural expansion, though farmers faced economic hardship through cycles of drought and depression. The 1930s Dust Bowl devastated many communities. Federal water projects, including Missouri River dams constructed in the mid-20th century, brought irrigation, flood control, and hydroelectric power.
South Dakota's economy evolved throughout the 20th century, gradually diversifying beyond agriculture. Tourism emerged as a significant industry, centered around the Black Hills, Mount Rushmore (completed in 1941), and Badlands National Park. Today, South Dakota combines agricultural tradition with sectors including finance, healthcare, and manufacturing while addressing ongoing reconciliation with its indigenous nations.
Major cities in South Dakota
- Sioux Falls
- Rapid City
- Aberdeen
- Brookings
- Watertown
- Yankton
- Mitchell
- Huron
- Box Elder
- Spearfish
- Pierre
- Vermillion
- Brandon
- Harrisburg
- Tea
- Sturgis
- Madison
- Belle Fourche
- Dell Rapids
- Hot Springs
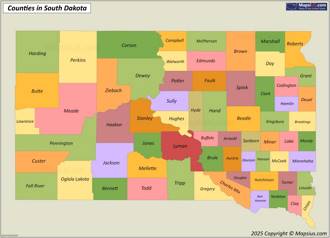
Counties in South Dakota
There are 66 counties in the U.S. state of South Dakota.
List of counties in South DakotaSouth Dakota County Map
Geography of South Dakota
South Dakota occupies 77,116 square miles in the North-Central United States, ranking 17th in size among all states. The Missouri River bisects the state diagonally from northwest to southeast, creating two distinct physiographic regions. The western portion belongs to the Great Plains, while the eastern section forms part of the Central Lowlands.
The Black Hills dominate southwestern South Dakota, rising abruptly from the surrounding plains. Harney Peak, reaching 7,242 feet, marks the state's highest elevation. This isolated mountain range contains valuable mineral deposits, dense forests, and distinctive geological formations like the granite spires of the Needles and the limestone caverns of Wind Cave National Park. East of the Black Hills, the Badlands present a stark landscape of eroded buttes, pinnacles, and spires carved from ancient sedimentary deposits.
South Dakota's hydrography centers on the Missouri River system. Major tributaries include the Grand, Moreau, Cheyenne, Bad, White, and James rivers. The eastern region contains numerous glacial lakes, with Big Stone Lake and Lake Traverse forming part of the state's northeastern boundary.
The state experiences a continental climate with extreme seasonal temperature variations. Winters bring bitter cold, with January temperatures averaging 10°F in the north and 22°F in the south. Summers feature hot conditions, particularly in the central and southern regions, where July averages exceed 85°F. Annual precipitation ranges from 25 inches in the southeast to less than 15 inches in the northwest, with most rainfall occurring during the growing season. The climate supports shortgrass prairie in the west and tallgrass prairie in the east, though much native vegetation has yielded to agricultural development.
South Dakota's geographical position exposes it to frequent weather extremes. The state records approximately 30 tornadoes annually, primarily in the eastern counties. Blizzards, drought cycles, and severe thunderstorms characterize the regional climate patterns. These environmental conditions have significantly influenced settlement patterns, economic development, and cultural adaptations throughout the state's history.
Below you will find a list of the largest lakes, the longest rivers, and the highest mountains in South Dakota.
Major Rivers in South Dakota
- Missouri River - 2,341 mi (3,767 km)
- James River - 710 mi (1,140 km)
- White River - 580 mi (930 km)
- Niobrara River - 568 mi (914 km)
- Big Sioux River - 419 mi (674 km)
- Cheyenne River - 295 mi (475 km)
- Belle Fourche River - 290 mi (470 km)
- Little Missouri River - 274 mi (441 km)
- Grand River - 200 mi (320 km)
- Moreau River - 200 mi (320 km)
- Bad River - 161 mi (259 km)
- Cherry Creek - 120 mi (193 km)
- Vermillion River - 97 mi (156 km)
- Little White River - 97 mi (156 km)
- Rapid Creek - 86 mi (138 km)
- Keya Paha River - 80 mi (129 km)
- Ponca Creek - 70 mi (113 km)
- Elm River - 60 mi (97 km)
- Redwater River - 52 mi (84 km)
- French Creek - 50 mi (80 km)
Major Lakes in South Dakota
- Lake Oahe - 578 sq mi (1,497 km2)
- Lake Francis Case - 159 sq mi (412 km2)
- Lake Sharpe - 87.5 sq mi (227 km2)
- Lewis and Clark Lake - 49 sq mi (127 km2)
- Lake Thompson - 28 sq mi (73 km2)
- Bitter Lake - 23.4 sq mi (60.6 km2)
- Big Stone Lake - 19.7 sq mi (51 km2)
- Lake Traverse - 17.2 sq mi (44.5 km2)
- Belle Fourche Reservoir - 12.5 sq mi (32.4 km2)
- Lake Poinsett - 11.7 sq mi (30.4 km2)
- Lake Kampeska - 7.8 sq mi (20.2 km2)
- Shadehill Reservoir - 7.8 sq mi (20.2 km2)
- Waubay Lake - 7.2 sq mi (18.6 km2)
- Lake Albert - 7 sq mi (18.2 km2)
- Angostura Reservoir - 7 sq mi (18.2 km2)
- Lake Madison - 4.4 sq mi (11.3 km2)
- Enemy Swim Lake - 3.4 sq mi (8.7 km2)
- Lake Hendricks - 2.5 sq mi (6.5 km2)
- Clear Lake - 2.3 sq mi (6.1 km2)
- Lake Herman - 2.1 sq mi (5.5 km2)
The Highest Mountains in South Dakota
- Harney Peak (Black Elk Peak) - 7,242 ft (2,207 m)
- Bear Mountain - 7,166 ft (2,184 m)
- Crooks Tower - 7,137 ft (2,175 m)
- Terry Peak - 7,064 ft (2,153 m)
- Crows Nest Peak - 7,048 ft (2,148 m)
- Odakota Mountain - 7,040 ft (2,146 m)
- Green Mountain - 7,000 ft (2,134 m)
- Flagstaff Mountain - 6,930 ft (2,112 m)
- White Tail Peak - 6,920 ft (2,109 m)
- Deer Mountain - 6,890 ft (2,100 m)
- Medicine Mountain - 6,878 ft (2,096 m)
- Cement Ridge - 6,674 ft (2,034 m)
- Spearfish Peak - 6,640 ft (2,024 m)
- Crow Peak - 6,600 ft (2,012 m)
- Custer Peak - 6,562 ft (2,000 m)
- Inyan Kara - 6,360 ft (1,939 m)
- Bear Butte - 4,426 ft (1,349 m)
- Eagle Mountain - 4,300 ft (1,311 m)
- Sheep Mountain - 3,806 ft (1,160 m)
- Thunder Butte - 3,281 ft (1,000 m)
Page Navigation
References
1. ^ Quick Facts South Dakota. U.S. Census Bureau.2. ^ "American Values Atlas: Religious Tradition in South Dakota". Public Religion Research Institute.


